If your website wasn’t launched a week ago and has been online for some time now, there are low-hanging fruit SEO opportunities you may have yet to be aware of.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the 9 go-to optimization techniques, which we’ll move the needle for you in getting more organic traffic to your website.
But first things first. What exact “fruits” are we talking about here?
Table of Contents
What is the low-hanging fruit in the SEO realm?
These are potentially some quick wins you definitely should take advantage of.
We distinguish the following categories for the low-hanging fruit SEO opportunities:
- Content-related.
- Technical SEO-related.
- Link building-related.
In many cases, some of these low-hanging fruits are pure nuggets accumulated over time, and now they are for harvesting.
How to Find Low-Hanging Fruit Opportunities for SEO
In a nutshell, you need to:
- Look at your pages with some rankings on Google and pay attention to those, not in the first positions or on the first page.
- Look at the insights inside your Google Search Console property and see specific phrases visitors use to visit your site, ones found on search engines.
- Check-in with the page load speed-related factors.
- Double-check whether your structured data is rich and sufficient.
- Revise your internal links.
- And some more.
But let’s dive deeper into the 9 go-to SEO strategies we announced in the beginning. These strategies will allow you to leverage the power of the SEO low-hanging fruit concept.
1. Low-hanging fruit keywords inside your existing content
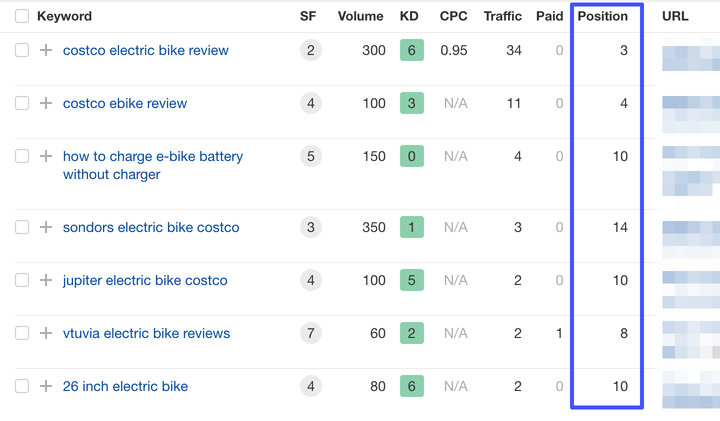
These are keywords that your website is already ranked for but not in Google’s top yet.
How to find low-hanging fruit keywords
In this example, we’ll be using Ahrefs. Here’s how you can do it:
- Inside the Ahrefs Site Explorer tool, while looking at your site’s SEO metrics, go to the “Organic Keywords” section, where you’ll find a list of keywords your website ranks for.
- Apply a filter to identify keywords currently ranking beyond the top 1 (e.g., positions 2-15).
- Review the search volume and keyword difficulty for these keywords. Look for keywords with moderate to high search volume and relatively lower keyword difficulty.
- Analyze the search intent behind these low-hanging keywords and assess if they align with your website’s content and target audience in the first place.
In this way, you can uncover keywords that are already bringing some organic traffic but have the potential for improvement. Targeting these low-hanging fruit keywords can help you boost your website’s visibility and attract more traffic.
2. Low volume and long tail keywords inside your Google Search Console

Long-tail keywords are longer and more specific search queries with lower search volume but relevant intent and specificity. In Google Search Console, you can identify such keywords by analyzing the search terms that have led users to your website. These queries often contain more words and provide insights into the specific phrases people use to find your content. But those could also be short-tail keywords spelled differently by users.
To identify these opportunities, follow these steps:
- Inside your Google Search Console property, navigate to the “Performance” section.
- Look for the “Queries” or “Search Queries” tab, which displays the keywords users have searched for.
- Sort the data by impressions to identify the most relevant keywords for your pages.
- Scan through the list of queries and identify longer, more specific phrases that could be considered long-tail keywords or short ones which are still highly relevant but not much presented on your page.
3. Update long-published content
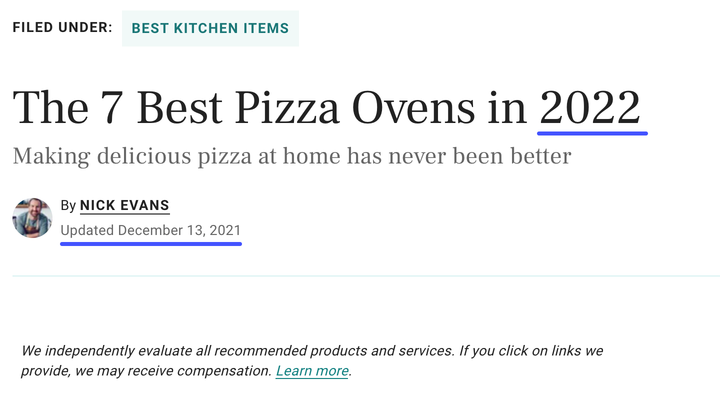
From a Search Engine Optimization standpoint, updating content ensures that your website stays relevant, up-to-date, and aligned with search engine algorithms.
Search engines prioritize fresh and relevant content. By updating your long-published page with new information, insights, or recent developments, you increase its relevance and demonstrate to search engines that your content is current and valuable to users.
When deciding which pages to update and what information to update them with, prioritize pages crucial to your website’s goals, such as high-traffic landing pages or pages targeting valuable keywords, or on the contrary – those pages showing dips in the relevant traffic.
- Focus on updating information that directly impacts your users’ needs and aligns with your website’s purpose.
- Ensure the data titled with the past year is updated with the current year.
- Take the time to thoroughly assess and analyze your older content, meticulously examining each piece to identify what crucial elements may be missing from its current composition. By conducting a comprehensive content audit and scrutinizing various aspects such as relevance, accuracy, comprehensiveness, and engagement, you can gain invaluable insights into the specific gaps that need to be filled to breathe new life into your previously published material.
4. Updating images

Images are also content on your web page. Hence, it would be best if you kept them actual too.
When doing an upgrade of the page, you can even go as far as reviewing and re-uploading the images to reflect the current year.
This one is much rare, but it adds up to Google’s love for maximum fresh and up-to-date content. Why not use it, then?
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, the images are uploaded inside the folder, which follows the structure ‘uploads/year/month/image_filename.jpg’.
When Google crawls the links with your images in 2023, it experiences the image with 2022 in the URL slug as a dated asset.
If you’re serious about the highest possible performance for a particular lucrative page, you can also utilize this tactic.
But also, you can ensure the image file names and ALT texts are descriptive and relevant to the content.
5. Schema Markup
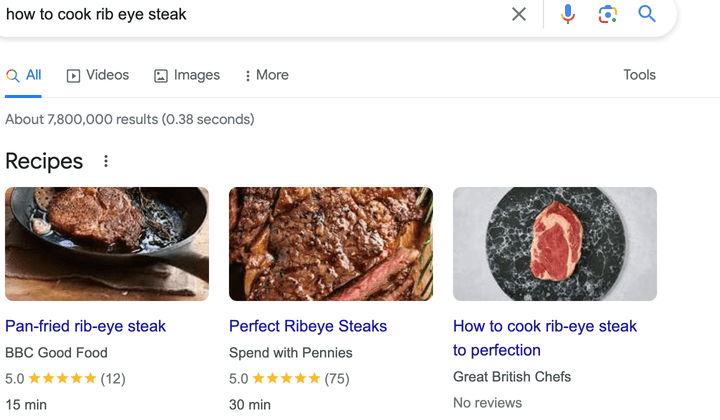
Even nowadays, Schema Markup is an often overlooked SEO opportunity that can improve your results.
It involves adding structured data to your website’s code, providing search engines additional context about your content. In the case of a lot of CMS, this feature can be installed under the hood but often requires some particular tweaks to make it work to the full extent.
By implementing Schema Markup, you can enhance the visibility of your web pages in search results with rich snippets, which are visually appealing and contain relevant information upfront.
In particular: featured snippets, review snippets, recipe snippets, event snippets, people also ask snippets, video snippets, local business snippets, and book snippets.
This can improve the click-through rate and attract more targeted traffic to your site. Schema Markup is relatively easy to implement and offers a competitive advantage by making your website more appealing and informative to search engines and users. Take advantage of this low-hanging fruit opportunity to boost your SEO efforts.
We can quickly research your Schema Markup situation as a part of our free SEO Video Audit here →.
By the way, if you’re looking to delve deeper into the differences between Technical SEO and Content SEO, our blog post on “Technical SEO vs. Content SEO – Understanding the Key Differences” provides valuable insights. Explore how these two crucial aspects of SEO work together to elevate your website’s performance.
6. Internal Linking
Proper internal linking is crucial in SEO. It allows “the juices to flow”.
It improves search engine crawlability, website navigation, and user experience. Internal links connect different pages within your site, helping search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your content.
They also distribute link authority throughout your website, guiding search engines to essential pages and improving their chances of ranking higher. Additionally, internal links provide pathways for users to discover related content, increasing their engagement and time spent on your site.
Look at a single internal link as a strategic move towards enhancing your website’s user experience and SEO performance.
How to place internal links on the site?
- Identify key pages. Start by identifying the most essential pages that you want to rank higher. These can be your cornerstone content or landing pages.
- Determine relevant anchor text: Choose anchor text that accurately describes the destination page and incorporates relevant keywords. This helps search engines understand the context and topic relevance.
- Look for opportunities to naturally link from relevant blog posts, articles, or other content pieces to your key pages. Ensure the linking content is related and provides additional value to the user.
7. Eliminate or remove pages with zero or low traffic
Many websites nowadays are bloated, full of pages that do not add value to the reader and don’t serve a particular purpose. Google has a crawl budget, and it’s limited. It is the number of pages that Googlebot – the web crawling bot- is willing to crawl and index on your website within a given timeframe.
So, it’s reasonable to have only the most valuable and required pages and articles on your website.
The algorithm here will be simple:
- Crawl your website using Screaming Frog (connecting it to the Google Analytics 4 and Google Search Console APIs).
- Export the results as a CSV file.
- Filter the top row with the column names.
- Go to the GA4 Views column and filter it by “Blanks” or “0”.
- Do the same for the “Impressions” column.
- Now look at the filtered pages and decide which are just deadweight and which makes sense to consolidate with other relevant pages.
8. Page speed
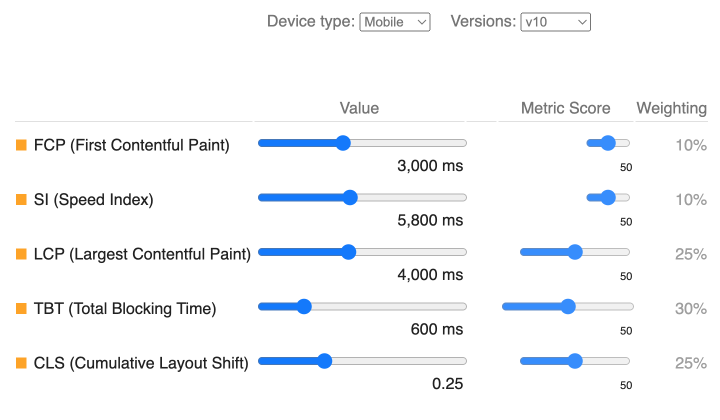
No need to say how vital page speed is nowadays, especially on mobile devices. Some of your pages may get poor SEO performance simply because of their long loading times.
To take advantage of this opportunity, follow these standard best practices:
- Analyze: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to measure your particular pages’ speed and identify areas for improvement.
- Optimize images: Compress and resize images, preferably have them in WebP format, and leverage lazy loading technology.
- Enable caching (if not yet): Configure caching headers and implement browser caching to store static resources locally.
- Minify code: Reduce CSS and JavaScript file size by removing unnecessary characters and spaces.
- Eliminate render-blocking resources: Optimize the loading of CSS and JavaScript to avoid delays in page rendering.
Obviously, these Technical SEO opportunity is deeply tech stuff to tackle with. Hence engaging a developer is required here.
Monitor and test: after optimizing existing pages, regularly monitor your website’s new pages’ speed and adjust accordingly.
9. Empty brand mentions
Empty brand mentions are instances where your brand is mentioned on the web without a link back to your website. To take advantage of it, follow these steps:
- Identify mentions: Use tools like Google Alerts, Mention, or Content Explorer inside Ahrefs to track mentions of your brand across the web.
- Reach out: Contact the website owners or authors who mentioned your brand without a link and kindly request that they add a link to your website.
- Provide resources: in case they are non-collaborative, if the link prospect looks really enticing and worth it, you may offer valuable content, infographics, or other resources, that the website owner can use to enhance their content while including a link back to your site.
By capitalizing on empty brand mentions, you can acquire pretty decent backlinks at times, improve your website’s authority, and enhance your overall SEO strategy.
In conclusion, low hanging fruit SEO offers a treasure trove of untapped opportunities to boost your website’s visibility and, ultimately, performance. You can make significant strides in search engine rankings and user engagement by leveraging the above techniques.
Pay attention to these easily achievable opportunities that can deliver remarkable results. Take action today and reap the benefits of low-hanging fruit SEO to propel your online presence to new heights.